What’s the difference?
Hi everyone! Today we will be talking about two accounts in the Central Provident Fund (CPF), the Ordinary Account (OA) and the Special Account (SA). These two accounts contribute to two of three basic needs in retirement; a fully paid-up home and a steady stream of lifelong retirement income. For Singaporeans and Permanent Residents, it is a useful tool for planning for our future. Want to find out more? Let’s dive right in!
CPF Contribution and Allocation Rates
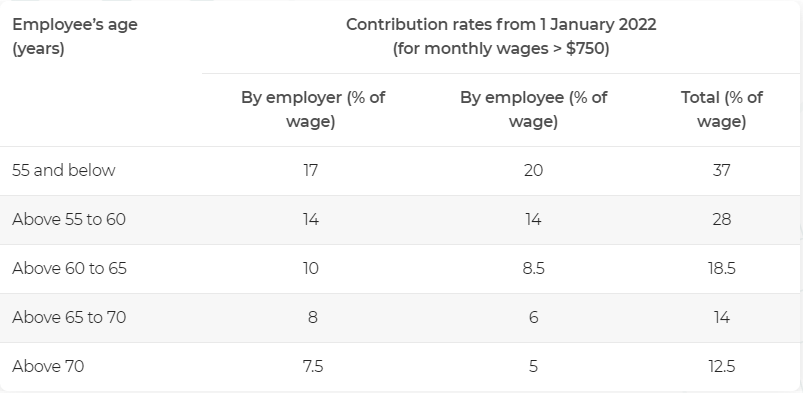
Before we talk about the OA and SA, let us cover the CPF contribution and allocation rates. You might ask, what are they? The Contribution Rates is the % of wages that both the employer and employee contributes to your CPF account. This % varies based on age.
As can be seen from the table below, the contribution rate is 37% for those 55 and under and it decreases with age.
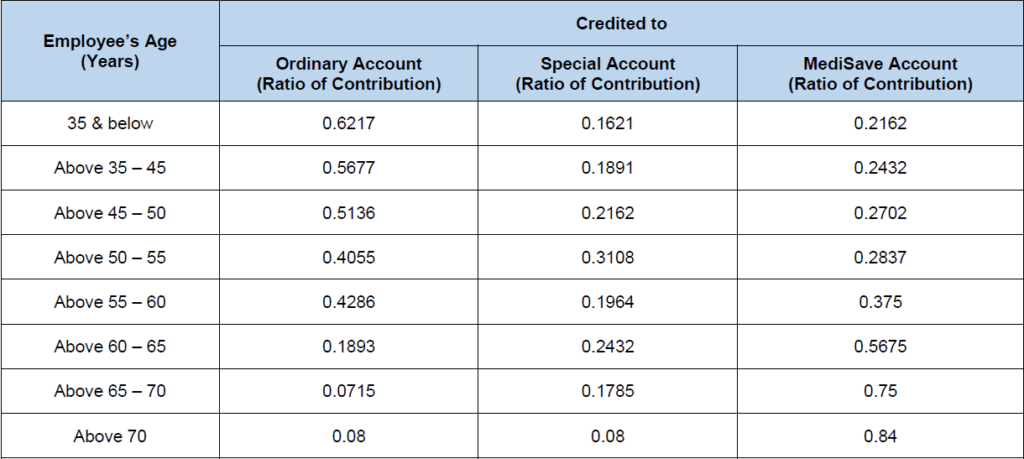
Conversely, the allocation rate is the ratio of contributions allocated to OA, SA and MediSave accounts. Taking a look at the table below, the ratio contributed to OA goes down with age, while the ratio contributed to MediSave increases with age. For SA, the contribution ratio increases with age, but peaks at the 50 – 55 age range before decreasing with age. The rationale for such ratios is based on the purpose of such accounts, which we will cover more in the next section!
What is Ordinary Account (OA)
The first account that most younger people will care about is the Ordinary Account (OA). OA is an account that is used for these few main goals; retirement, housing, insurance, education and investment.
The monies in your OA earns a 2.5% p.a. and is compounded annually. In addition, for the first 20k in your OA, you can earn an additional 1% per annum of interest if you are 55 years and below. However, the extra interest earned on OA savings will go into SA or retirement account (RA) instead. We will cover more on this extra interest when we talk about SA.
Uses of OA
Now, let us cover the various uses of OA:
Retirement

Firstly, OA can be used to save for retirement. At age 55, your retirement account (RA) will be formed. RA is formed by transferring savings from SA to the RA. If your SA funds fall short of the FRS, funds from OA will be used to supplement and form the FRS. Depending on the amount in your RA, you will receive monthly payouts for life (from 65 years old) under the CPF LIFE scheme. I won’t go into detail on RA and the payouts in this post, however, if you would like me to do so in the future, do let me know in the comments below!
Housing
Next, the funds in your OA can be used for housing as well! Your OA savings can be used to buy a HDB flat, or buy or build private and residential properties in Singapore. It can be used for down payment and housing loan taken for the property purchase, stamp and legal fees, loan taken for the construction of your house and the purchase of vacant land (for private properties only), as well as Home Protection Scheme premiums (for HDB flats only).

Do note that depending on the type of housing, there are certain restrictions and caps on the amount (or %) that can be used from OA. I will link the conditions below if you would like to find out more.
However, one thing we should be aware of when using OA savings to pay for housing is the CPF refund when selling or transferring your property. When selling your property (that you used CPF to buy for), the sales proceeds will be used to pay off the outstanding housing loan taken to buy the property and refund the CPF amount used for your property. The refund amount is the principal amount of CPF used + the interest accrued. For the full refund details, you can find it here. I think this is something to consider before using OA to pay for housing, especially if one is planning on selling the property in the future.
Insurance
Another use of OA is to pay for insurance coverage. One common insurance is the Dependents’ Protection Scheme (DPS), which provides coverage against death, terminal illness and total permanent disability. While the scheme is not compulsory, you would have to opt-out on your own as it is automatically extended to everyone between the ages of 21 – 65 upon their first CPF contribution.
For HDB owners, another insurance that can be paid for with OA is the Home Protection Scheme (HPS), which protects you and your loved ones from losing your Housing and Development Board (HDB) flat in the event of death, terminal illness, or total permanent disability.
Education
For many, we would want to continue our studies through tertiary education. Worried about how we can pay for our education? Fret not! Under the CPF Education Loan Scheme, you can use OA savings to pay for your education. However, there are some constraints to it:

- How much OA savings can I use?
You can use your OA savings up to the Available Withdrawal Limit (AWL). The AWL is either 40% of accumulated OA savings or the remaining OA balance, whichever is lower.
However, for those 55 years and above, the FRS must be set aside before using the remaining savings in the OA up to the AWL.
- Who can I use the OA savings on?
OA savings can be used on your own, children’s, spouse’s, siblings’ or relatives’ tuition fees.
- What can I use the OA savings on?
For OA savings, the CPF Education Loan Scheme covers all approved full-time subsidised undergraduate courses leading to a degree. The scheme covers all the undergraduate courses in publicly funded autonomous universities. In addition, it covers full-time subsidised diploma courses. For more details, you can find them here.
Investment
Lastly, we can use our CPF OA to invest under the CPF Investment Scheme (CPFIS). To invest CPF OA (and SA) one would need to meet the following conditions:
- are at least 18 years old;
- are not an undischarged bankrupt;
- have more than $20,000 in your OA; and/or
- have more than $40,000 in your SA; and
- have completed the CPFIS Self-Awareness Questionnaire (SAQ) (applicable to new investors with effect from 1 October 2018)
For OA savings, you can only invest up to 35% and 10% of investible savings* in stocks and gold respectively.
* Investible savings refers to the sum of your OA balance and the amount of CPF you have withdrawn for investment and education.
If you are wondering what you can invest your OA savings in under CPFIS, I have indicated the full list of securities below:
| Investment products included under CPFIS | Ordinary Account (OA) | Special Account (SA) |
|---|---|---|
| Unit Trusts (UTs) | Yes | Yes Higher risk UTs are not included |
| Investment-linked insurance products (ILPs) | Yes | Yes Higher risk ILPs are not included |
| Annuities | Yes | Yes |
| Endowment policies | Yes | Yes |
| Singapore Government Bonds (SGBs) | Yes | Yes |
| Treasury Bills (T-bills) | Yes | Yes |
| Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs) | Yes | No products currently available Higher risk ETFs are not included |
| Fund Management Accounts | Yes | No |
| Fixed Deposits (FDs) | No products currently available | |
| Statutory Board Bonds | No products currently available | |
| Bonds Guaranteed by Singapore Government | No products currently available | |
| Up to 35% of investible savings can be invested in: | ||
| Shares | Yes | No |
| Property Funds | Yes | No |
| Corporate Bonds | Yes | No |
| Up to 10% of investible savings can be invested in: | ||
| Gold ETFs | Yes | No |
To invest CPFIS OA savings, you would need to open a CPF Investment account with the following CPFIS agent banks with your CPF statement:
- DBS Bank Ltd (DBS)
- Overseas-Chinese Banking Corporation Ltd (OCBC)
- United Overseas Bank Ltd (UOB)
Another way to invest would be using a robo-advisor. At the time of writing, only Endowus allows you to invest your CPF OA savings. However, you do need to meet the requirements above before you are eligible to invest with them.
What is Special Account (SA)
On the other hand, the Special Account (SA) is for old age and investment in retirement-related financial products. Unlike the OA, you will earn a higher interest of 4.0% p.a. compounded annually on your CPF balances. This is much higher than the 2.5% interest in your OA account!!!
(To put things in perspective, using the CPF Ordinary Account-Special Account Savings Transfer Calculator, you are projected to earn an additional $2000 just from transferring $10,000 from OA to SA. The amount gets even larger for even longer periods due to the power of compounding.)
As previously mentioned, for those aged 55 and under, you will receive an additional 1% per annum interest on the first $60k (capped at $20k for OA). This means that you can get up to 5% (4% base from SA + 1% additional interest) on the first 60k of your CPF balances.
For those 55 and up, they will get an extra 2% per annum on the first 30k, and an extra 1% per annum on the next 30k. For those interested, you can read more here.
Uses of Special Account
When it comes to uses of SA, it is much more limited compared to one’s OA account. However, there are still some uses of SA in addition to the bonus interest rate you get!
Investment
As mentioned previously when covering uses of OA, your SA can be used for investing purposes too! However, do be aware that you can only invest your SA savings above the 40k saved in your SA account. Compared to the investment options in OA, it is comparatively much more limited. Here is the list of securities you can invest in:
| Investment products included under CPFIS | You can invest using your CPF savings from SA |
|---|---|
| Unit Trusts (UTs) | Yes Higher risk UTs are not included |
| Investment-linked insurance products (ILPs) | Yes Higher risk ILPs are not included |
| Annuities | Yes |
| Endowment policies | Yes |
| Singapore Government Bonds (SGBs) | Yes |
| Treasury Bills (T-bills) | Yes |
| Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs) | No products currently available Higher risk ETFs are not included |
| Fund Management Accounts | No |
In addition, SA does not support investing with robo advisors (Endowus to be specific) unlike savings from OA accounts.
However, unlike CPFIS-OA, for CPFIS-SA, you do not need to open a CPF Investment Account to invest your SA savings. You would just need to approach the product providers directly to buy or sell your investments.
Tax-relief (Central Provident Fund (CPF) Cash Top-up Relief)
Another use of SA is to maximise your tax reliefs! You can make a cash top-up of up to $8,000 per calendar year for you and an additional $8,000 per calendar year for your loved ones to your SA (or MediSave Account) and enjoy a tax relief equivalent to the amount of cash top-ups made. Do note that there are a few criteria to qualify for the tax relief as follows:
- The tax relief cap for cash top-ups to Special Account (SA) and Retirement (RA) will be shared with top-ups to MediSave Account for employees*. Learn more about the tax relief changes from 1 January 2022.
- For cash top-ups to self and your loved ones, tax relief only applies to cash top-ups up to the current Full Retirement Sum (FRS). Log in with your Singpass to see how much you can top up to yourself.
- Your loved ones include parents, parents-in-law, grandparents, grandparents-in-law, spouse and siblings.
- If you are making cash top-ups for a spouse or sibling, you will only be eligible for the tax relief if the recipient’s income in the previous year does not exceed $4,000 or if the recipient is handicapped^. In this instance, income would include income from bank interest, dividend and pension, investment income/rental income/directorship income. An example of a handicapped person is someone with visual-impairment, loss of hearing, loss of limb and dementia.
- If you are making a cash top-up to employee, you will be eligible for an equivalent amount of tax deductions for the cash top-ups made, while your employee will also receive tax relief of up to $8,000 per calendar year. The tax relief that your employee will receive takes into consideration any cash top-ups that he or she has made to own CPF accounts.
- There is a personal income tax relief cap of $80,000, which applies to all tax reliefs, including tax relief on cash top-up made to your CPF accounts.
Depending on your income tax rate, this can yield significant income tax savings and may be an option for you to consider.
Final Thoughts
Now that we have come to the end of the post, I would like to congratulate you for sticking to the end! While this topic is rather content and specifics heavy, I hope that you have managed to get a better idea of how to leverage your OA and SA accounts to plan for your future. As there are many resources used throughout this article, I would like a few of the most important ones if you would like to find out more.
As always, thank you all for reading and if you enjoyed do support by sharing this post with those who might need it too. Cheers!
List of useful links/resources
- CPF Overview
- CPF Investment Scheme (CPFIS)
- Self-Awareness Questionnaire (To assess the suitability of CPFIS)
- CPF Education Loan Scheme

– Rice




What an insightful read! I did not know that SA contributions can help reduce our taxable income! thanks for sharing rice!
Hey! Glad to share on the tax-relief benefits associated with CPF. Thanks for your support : )